Why NSW for copper
- Second largest Economic Demonstrated Resource (EDR) in Australia
- More than 11 Mt in current copper resources
- The Macquarie Arc in the Lachlan Orogen is a world-class region for exploration
- Established copper mining jurisdiction with 7 operating mines
- More than 15 projects in development
Overview
Copper is one of the world's most important metals for general domestic use and in renewable technologies as it conducts heat and electricity more efficiently than many other metals. It is essential for renewable energy systems including solar, hydro, thermal and wind energy and underpins transmission infrastructure.
Copper’s use in consumer goods, construction, transport, industry, and infrastructure, especially power generation and transmission, means that demand is closely tied to world economic growth.
Copper will play a critical role in the global renewable energy transition. In 2024, around 30% of copper demand was for new energy technologies and electrification, and by 2030 this could be around 35% (Source: IEA).
In mid 2025, the London Metal Exchange copper price was $9,765 per metric tonne, by the year 2035 the price is forecast to increase to $12,050 per metric tonne. World prices are expected to remain historically high out to 2029-30 as demand continues to grow, driven by the transition to net zero and its use in renewable energy infrastructure, rising usage in consumer appliances and construction of data centres for use in AI.
Estimated copper supply is expected to increase from 27 million tonnes to 32 million tonnes. Overall copper demand is forecast to increase from 27 million tonnes to 32 million tonnes by 2030 (Source: IEA). Copper supply is struggling to keep pace with demand as new mines are slow to develop and trade barriers impact on copper scrap supply.
In NSW, large reserves of copper and strong mining industry present investors with many opportunities to capitalise on the significant increase in copper demand.
NSW resource
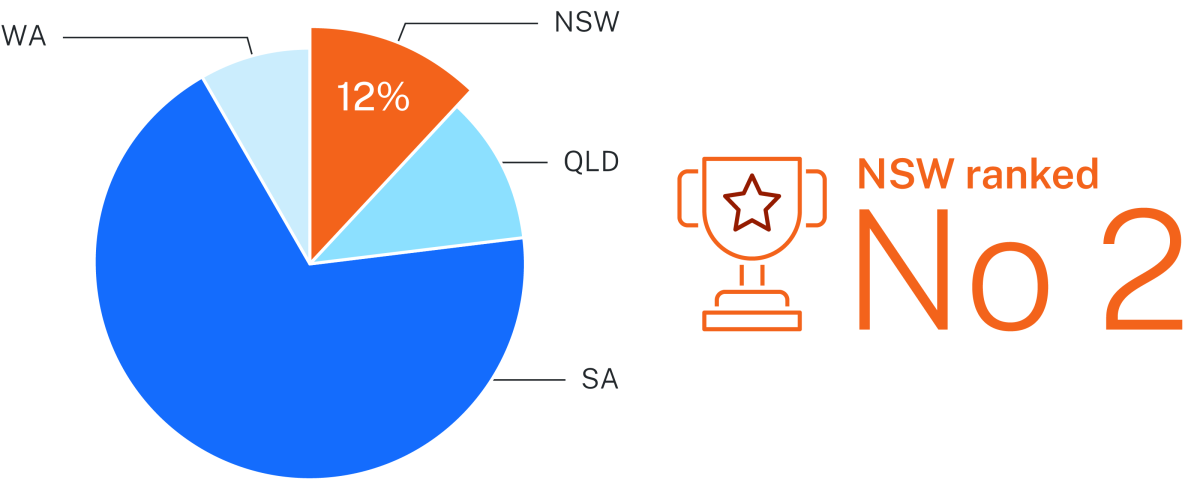
NSW is ranked second in Australia for copper contained EDR resources, holding 13% of Australia’s EDR for copper (Source: Geoscience Australia, Australia's Identified Mineral Resources 2024.
NSW has a diverse range of copper-rich deposits where copper is produced as either the principal commodity (Northparkes, CSA and Tritton mines) or as a by product with copper credits from mining concentrates.
Copper mineralisation in NSW is predominantly associated with the world-class Macquarie Arc and Cobar Basin in the Lachlan Orogen. Copper-enriched systems in this region include the porphyry copper-gold and related skarn deposits, such as the Cadia district (Cadia East) and the Northparkes, Copper Hill and Temora districts. The New England Orogen and Broken Hill region are also prospective for copper.
NSW remains under-explored for copper, particularly in areas under cover without basement exposure where cover depths are less than 500 m. There are a range of opportunities for new discoveries, especially in the Macquarie Arc which has the highest density of known and predicted undiscovered deposits. Drilling beneath known mineralisation along the eastern margin of the Cobar Basin has consistently met with exploration success.
Copper in NSW map
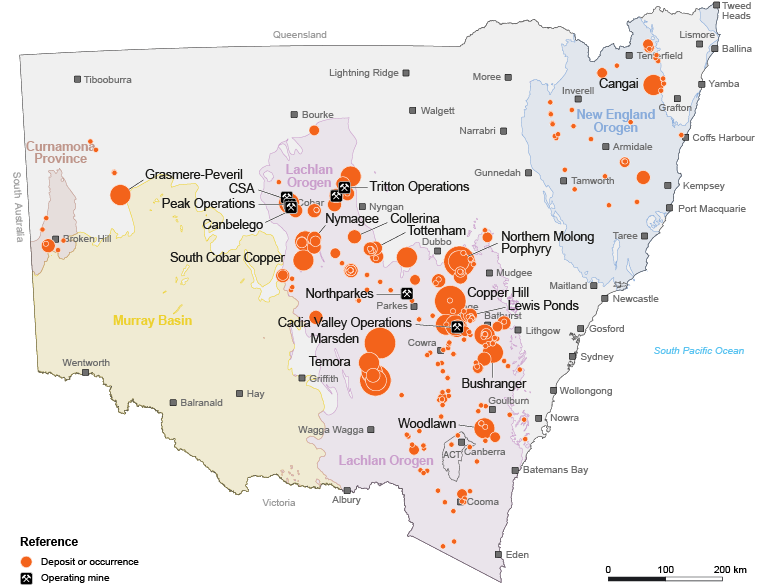
Download the Copper in NSW map (PDF, 3.07 MB).
Essential uses

Electrification and transmission |
Solar PV |

Wind turbines |
Electric vehicles and charging |

Electronics |

Scientific and medical instruments |
Quality data for explorers
NSW is known for its world class pre-competitive data, and has a long history of providing geological, geoscientific and geochemical data to promote investment in exploration.
Pre-competitive data to support copper exploration (and other commodities) is made freely available on the Geological Survey of NSW’s web map application MinView.
The NSW Government recently completed its largest ever geophysical survey acquisition program through airborne electromagnetic, airborne magnetic and radiometric, gravity, and deep crustal reflection seismic surveys. These surveys collected over 150,000 km2 of new data across the New England Orogen, the Lachlan Orogen and the Murray Basin areas that are prospective for critical minerals and high-tech metals, including copper.
Global overview
Global reserves are currently estimated to contain 980 Mt of copper (Source: USGS). Latin America (Chile and Peru) has the largest known copper reserves and is expected to remain the largest producer of copper for the foreseeable future.
Australia has the third largest reserves of copper in the world and is the world’s eighth largest producer with 27 operating copper mines producing 780,000 tonnes in 2023, with economic demonstrated resources over 104 Mt and 27 Mt in ore reserves (Source: USGS).
China is the largest producer of refined copper with over 40% of the world smelting capacity. China uses over half of the world’s refined copper.
Copper is an extremely recyclable metal able to be used multiple times without performance loss. Historically, 30% of world copper consumption was recycled copper.
2024 Global copper reserves – 980 million tonnes copper content
2024 Global copper production – 23 million tonnes copper content
Source for global overview content and charts: modified from USGS Mineral Commodity Summaries 2025.
NSW operating mines
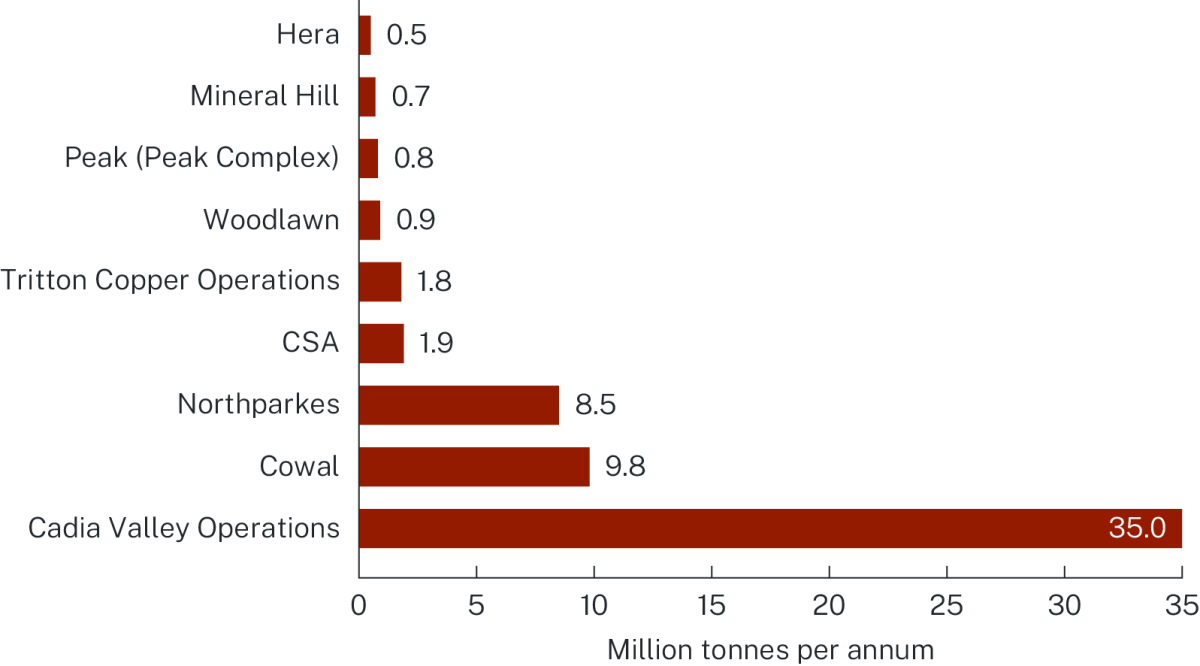
NSW is an established copper producer and Australia’s second largest copper producing state. Four of NSW’s copper mines are in Australia’s top 10 copper producing mines, including Cadia Valley Operations, CSA, Northparkes and Tritton Copper Operations.
NSW is experienced with hosting technically sophisticated mining operations and has shown leadership in the automation of underground operations using remote control methods. Australia’s first block cave operation was successfully developed in NSW, being the Northparkes mine, and this mining method is expected to play a key role in future production of lower ore grade sources. The Cadia Valley Operation isa highly productive gold and copper mine with a reputation for using advanced digital and resource technology applications.
Production in NSW
Over the past 5 years, NSW copper production has averaged nearly 187,190 tonnes a year. NSW copper production from existing mines is forecast to increase from 187,985 tonnes in 2024-25 to 194,182 tonnes in 2025-26. The 2024-25 financial year copper production in NSW was 187,985 tonnes.
Major copper mine production

Processing in NSW
Many of the copper operations in NSW have established processing plants to produce copper concentrates (or similar) ready for further refining or smelting. There are a number of plants across the Cobar region that currently have capacity to increase mill throughput, presenting opportunities for industry partnerships (such as processing of third-party feedstock).
Copper processing plants and capacity
NSW project highlights
NSW is well positioned to bring on new supply of copper with a strong pipeline of projects at varying development stages and advanced exploration stage. There have been successful project expansions, with recent inventory growth including at Northparkes (a cluster of porphyry deposits). In the 2023-3024 financial year copper exploration expenditure in NSW totalled $96 million.
At the greenfield stage, the recent Boda–Kaiser porphyry (Northern Molong Porphyry project) highlights the NSW Central West region’s exploration potential for large tonnage copper gold resources. NSW has a strong pipeline of opportunities and exploration potential in key regions that will allow the state to remain a leading copper producer for the future.
| Project (deposit) |
Contained Cu ('000 t) |
|---|---|
| Bushranger Copper-Gold |
1,034 |
| Canbelego Copper |
32 |
| Cangai Copper |
114 |
| Collerina |
41 |
| Constellation (Tritton Operations) |
153 |
| Copper Hill |
520 |
| Drake |
16 |
| Gilmore |
1,150 |
| Koonenberry (Grasmere–Peveril) |
60 |
| Lewis Ponds |
88 |
| Marsden |
560 |
| Myall |
297 |
| Northern Molong Porphyry (Boda–Kaiser) |
1,460 |
|
South Cobar Copper
|
235 |
| Tottenham |
71 |
| Yeoval Porphyry |
49 |
| Total contained copper |
5,880 |
| Note: The contained copper totals are based on combined resources for that project (the amount of copper as a metal that is contained within one or more resources). Source: public company announcements. | |
Notes:
All percentages (including in the pie charts) are rounded to whole numbers.
Forecasts are based on NSW Resources’ interpretation of available information. Forecasts are inherently uncertain and should be seen as a guide only. Actual outcomes may be different.